Counter Actions Against BWAs
Referring to open-source reports, the suspicion of possession and development of biological agents and weapons remains high at certain countries. This is due to several factors, including the ubiquity of dual-use of biotechnologies, the small-to-indetectable physical footprint of sites for developing biological weapons, and ongoing WMD programs by several nations.
Biological weapons are not any more seen as “classic WMD tool in the battle fields”, their added value is the highest from the standpoint of grey-zone or hybrid warfare, and their potential as asymmetric, covert, assassination tools, and for providing regime security.
Potential Scenarios of Biological Agent Usage
The dispersion of biological agents can be conducted by spray devices and special ammunitions. Agents can also be spread by animal to human, human to human, insect to human or through vectors. Dispersion sprayers have to be optimised to generate the respirable range particles, and these devices can be mounted on vehicles, unmanned systems or places in a concealed location. Vectors can also be used for concealed biological agent dispersion and these vectors won’t be distinguished from the common insects, animal or human population of the area. In addition, other less effective methods like glass bottles, closed bags, or letters, can also be used for small scale dispersion.
A concealed attack may have more potential than a large scale and open biological attack. In a terrorist attack, at the beginning, the biological agent diluted clouds may be not recognised, and the same applies to poisoning of drinking water and foodstuff. Biological agent dispersion is very effective on environment conditions like wind, temperature, sun UV light, moisture, terrain and overgrowth.
Security and defence organisations have studied the following potential scenarios, as where biological agents’ dispersion may be encountered.
- Biological agent usage in urban areas, like shopping centers, critical infrastructures, transportation hubs and mass events. The pathway(s) the agents use for entering the human body can be skin (broken), eyes, lungs by inhalation, foodstuff, and drinking water. Typical agents in these scenarios may be toxins, viruses or bacteria.
- Biological agent usage in rural areas, like targeting against plants and livestock. Biological agents may be used in this way to disrupt the economy (example the foot-and-mouth disease virus, which caused widespread economic damage and public concern). The pathway(s) the agents use for entering the human body can be skin, eyes, lungs by inhalation, foodstuff, and drinking water. Typical agents in these scenarios may be toxins, viruses or bacteria.
- Biological laboratory, production or storage (legal, illegal) facilities release, accident, or sabotage. Example facilities can be common industrial, healthcare, university facilities or illicit laboratories or production sites. Biological facilities may release hazardous material to the environment. The pathway(s) the agents use for entering the human body can be skin, eyes, and lungs by inhalation. Typical agents in these scenarios may be toxins, viruses or bacteria. These agents may persist in the environment and inside the facilities from days to years, depending on the particular agent and on local conditions.
Effects of Biological Agents Usage
Biological agents and biological weapons are very attractive to sabotaging and terrorist usage because aerosols of biological agents are invisible, silent, odourless, tasteless, and are relatively easily dispersed. The production is relatively easy, using the common technology available for the production of some antibiotics, vaccines, foods, and beverages. Referring to some calculations, they are 600 – 2000 times cheaper than other weapons of mass destruction. Depending on the delivery mechanism, one kilogram of anthrax powder has capability to kill up 100 000 people, and the economy impact is estimated to be 26.2 billion dollars/ 100 000 exposed persons.
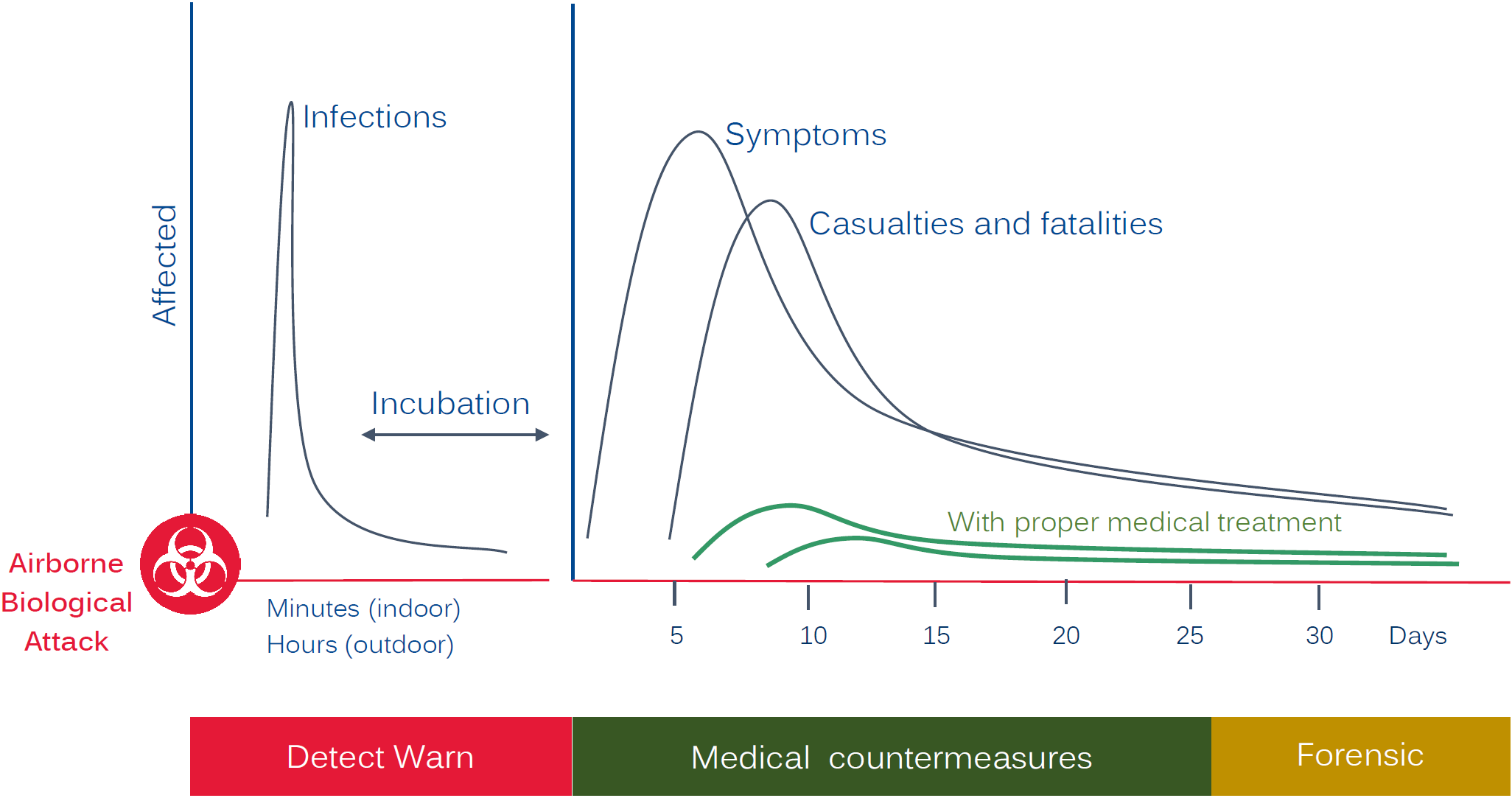
Timeline of a Biological incident showing how crucial it is to have early-warning detection.
The use of biological agents doesn’t have an immediate impact because of the delay between exposure and onset of illness. It’s unfortunately normal, that the first victims need to be identified by doctors and other healthcare officials, based on the first-wave of victims’ symptoms. They have to identify the organism, determine when and where the exposure occurred, and prevent more casualties by ordering mass vaccinations, prophylactic treatments, and infection control procedures.
Indications & Detection of Bio Agents Usage
The potential biological agents use indications and a biological outbreak of rare or new disease are a seasonal disease during an off-season time, an outbreak of diseases in a non-endemic area, a known pathogen with unusual resistance or unusual epidemiologic features, an unusual clinical presentation or age distribution, a genetically identical pathogen emerging rapidly in different geographical areas.
Early warning detection with systems and confirmation methods are vital to mitigate the biological agents usage effects and scale. Also, all other clues, like those shared by witnesses and victims, can provide important information in early outbreak stages. For an unusual event, associated potential clues are: highly unusual event with large numbers of casualties, higher morbidity or mortality than is expected, uncommon disease, unusual disease manifestation, lower attack rates in protected persons, point-source outbreaks, multiple epidemics, downwind plume pattern, dead animals, reverse or simultaneous spread of human and animal cases and direct evidence.
Protection Against Biological Agents
In normal daily life, we are potentially exposed to various biological agents. Some of the essential prophylactic protection and prevention measures include vaccination, cleanliness, personal hygiene and controlled intake of food and drinking water.
When facing a bio hazard and when airborne concentration is unknown or high, the recommended protection level is the highest. When the scene conditions are understood and the exposure is determined to be at lower level, the personal protection equipment level can be lower. An intentional biological agent release may cause secondary hazards, so, for first responders the basic protection equipment SCBA provides respiratory protection against biological agents.
Identification of Biological Agents
After the potential usage of a biological agent is detected, its presence should be confirmed or denied by using presumptive identification level tools. These tools and equipment are common field-level tools, like antigen antibody immunoassays. If the result is positive, it is recommended to take operational samples for further analysis in polymerase chain reaction-based systems. The highest level of biological agents identification is done with analysing samples in laboratory environment, tools and procedures.
Bio Decontamination
Biological decontamination / disinfection means rendering biological agents harmless. There are highly effective disinfection solutions suitable for carrying out this task.
Washing with water and soap removes nearly most of all biological agents. However, it does not kill the agents, therefore water runoff must be collected and treated before disposal.
For skin decontamination 0,5 % calcium hydrochloride or household bleach can also be used, which is an effective biological decontaminant. A 5% calcium hydrochloride solution is suitable for material and equipment decontamination not for skin. Other disinfection solutions are also recommended for biological decontamination.
If time is no critical factor and human life is not threatened, natural environment methods can be used for biological agents’ decay. Sunlight is especially effective against most biological agents. Warm, windy weather can significantly reduce contamination. Many variables affect the biological hazards and it is impossible to accurately predict how long it takes such contamination to decontaminate by natural ways.
ENVI Assay System
Bertin Environics’ ENVI Assay System bio defence tests is the ideal tool for provisional identification of Biological threats. These high quality and proven tests for early detection are the most compact immunoassay “lab-in-a-box” in the market.
Disposable, separate assays for seven highly poisonous hazardous agents: ricin toxin, botulinum toxin, Bacillus anthracis anthrax, orthopox virus, SEB, Yersinia pestis and Francisella tularensis.


Leave a Reply